 mhmd@verizon.net
| 11600 Wilshire Blvd, Ste 420, Los Angeles CA 90025
mhmd@verizon.net
| 11600 Wilshire Blvd, Ste 420, Los Angeles CA 90025
Resources
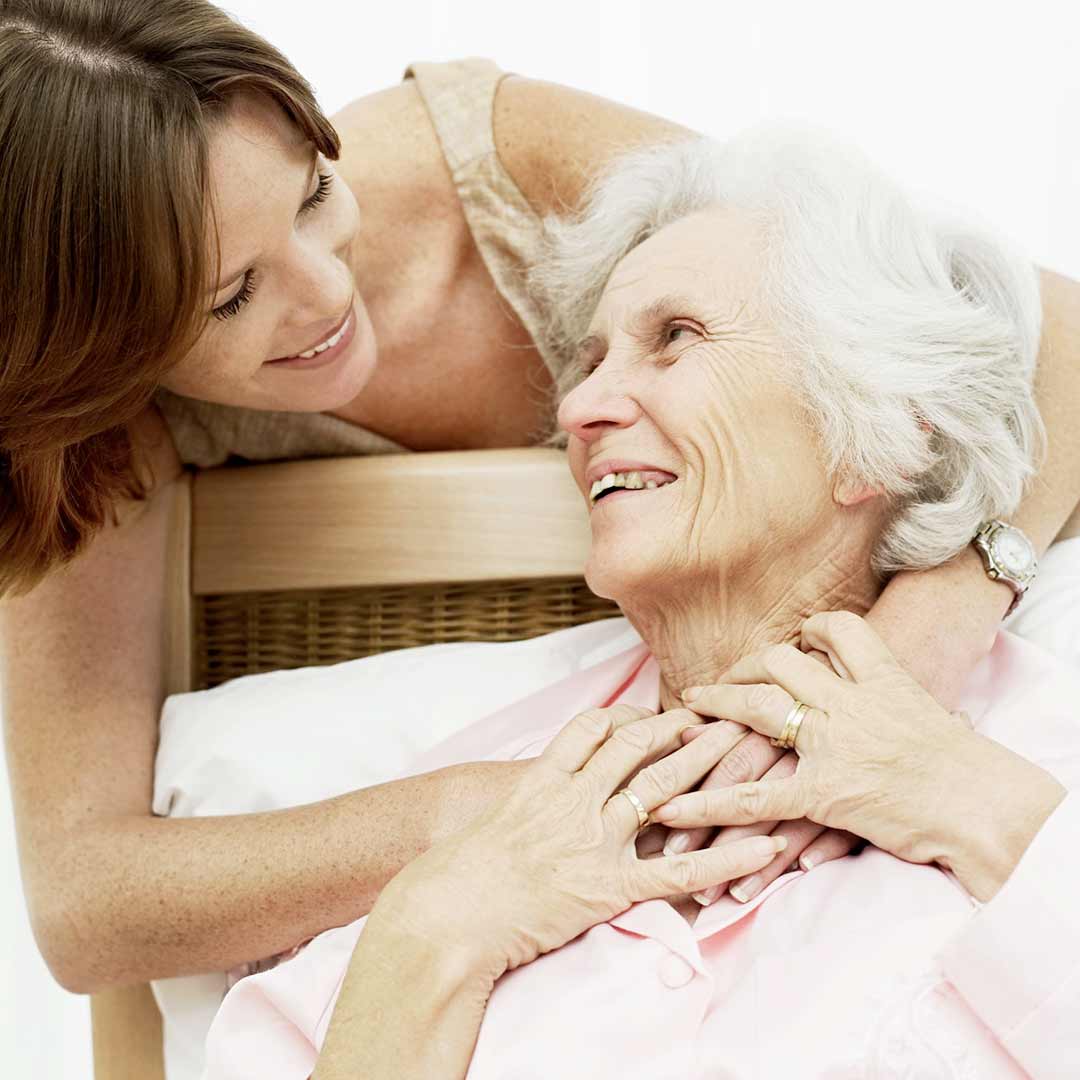
ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE IN LOS ANGELES, CALIFORNIA
Understanding Alzheimer's Disease
What Is Alzheimer's Disease?
Alzheimer's disease is a disorder that attacks brain tissue. Its main symptom is steadily increasing memory loss. Problems with vision, language, and emotional control are also common. These abilities may decline over 5 to 20 years. People with Alzheimer's disease will require constant care at some point.
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms usually begin with loss of recent memories. For example, you may unknowingly repeat stories in the same conversation, or you may forget certain events. Other symptoms include:
- Trouble Learning New Information
- Gradually Increasing Confusion and Disorientation
- Trouble Speaking in Conversations
- Personality and Behavioral Changes
- Misplacing Objects or Becoming Lost in Familiar Neighborhoods
- Problems with Judgment and Common Sense
Symptoms usually begin with loss of recent memories. For example, you may unknowingly repeat stories in the same conversation, or you may forget certain events. Other symptoms include:
- Loss of Interest in Usual Activities
- Distrust of Caregivers or Family Members
- Depression
- Moodiness
It is important to see a doctor when you suspect Alzheimer's disease symptoms. Only a doctor can diagnose your condition correctly.

What Causes Alzheimer's Disease?
The exact cause of Alzheimer's disease is unknown. What is known is that a brain affected with Alzheimer's disease is filled with deposits of a waxy substance called amyloid or plaque. Nerve cell connections in the brain are reduced, causing a loss of short-term memory. Other intellectual and physical functions are affected in time.
Some of these changes happen in normal aging. Far more change is found in people with Alzheimer's disease. Inherited or genetic factors and aging seem to play important roles.
Some of these changes happen in normal aging. Far more change is found in people with Alzheimer's disease. Inherited or genetic factors and aging seem to play important roles.
How Is Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosed?
There is no simple test to diagnose Alzheimer's disease. When Alzheimer's disease is suspected, it is important to have a complete medical and neurological evaluation. An evaluation may include:
- A Complete Health History and Physical Examination
- Tests of Blood and Urine
- Tests That Evaluate Thinking Skills and Memory
- Brain Imaging Scans
What Are the Treatments?
There is no known cure for Alzheimer's disease. There are medications that may help slow down or reduce symptoms.
These drugs block a brain chemical that breaks down acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is a key substance needed for brain cells to function properly. Some drugs may also reduce behavioral changes caused by the disorder.
These drugs block a brain chemical that breaks down acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is a key substance needed for brain cells to function properly. Some drugs may also reduce behavioral changes caused by the disorder.

Understanding Brain Injuries
What Is Brain Injury?
Each year in the United States, about 1.5 million people experience a brain injury. A blow or jolt to the head can cause a traumatic brain injury. You do not have to hit your head on an object to injure the brain. Sudden movement of the brain in the head, such as a whiplash injury due to a car accident, can cause a brain injury.
Brain injury is a major cause of death and disability. More US children die of brain injury than any other cause.
Brain injury is a major cause of death and disability. More US children die of brain injury than any other cause.
What Causes Brain Injury?
Half of all brain injuries are due to transportation-related accidents. About 20 percent of brain injuries are due to violence. This includes firearm use and child abuse. For people age 75 and older, brain injuries are most often caused by falls.
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms can be mild to severe. Some shows up right away. Others may appear several days or weeks after the injury. Symptoms include:
- Lack of Coordination
- Confusion
- Memory Problems
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea or Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Anxiety or Depression
- Change in Sleep Patterns
- Seizures
How Is Brain Injury Diagnosed?
Immediate emergency medical treatment is crucial. It is helpful to have a neurologist involved early in the diagnosis and treatment. It is even more vital if symptoms continue for more than a few days or weeks.

After an injury, emergency treatment is needed to control bleeding in and around the brain, control the amount of pressure in the brain, and make sure breathing, blood pressure, and other systems are stable. Then doctors can assess the severity of the brain injury. They check the person's level of consciousness and neurological functioning. Brain imaging tests may be used to help in the diagnosis.
What Are the Treatments?
The treatment and recovery process is different for each person. No two brain injuries are alike.
Emergency treatment begins at the time of the accident or incident. Medical personnel try to stabilize the person. About half of all severely injured people may need surgery. The surgery may be to remove or repair bleeding in or around the brain or to drain fluid from the brain.
Emergency treatment begins at the time of the accident or incident. Medical personnel try to stabilize the person. About half of all severely injured people may need surgery. The surgery may be to remove or repair bleeding in or around the brain or to drain fluid from the brain.
After emergency treatment, people may be in a hospital intensive care unit. Once they are stable, they may move to a regular bed in the hospital. Some people will need further help after leaving the hospital. Other people whose injuries do not require hospitalization may also need help to recover. Options for rehabilitation can include:
- Outpatient Therapy
- Home Health Services
- Independent Living Programs
The goal of rehabilitation is to help people regain the highest possible level of independent functioning. Rehabilitation should be tailored to each person. It should be based on the individual's strengths and capacities.

Call or email our neurology center in Los Angeles, California, for additional information on sleep studies and epilepsy treatments.
CONTACT INFORMATION
Phone: (310) 477-7201
Address: 11600 Wilshire Blvd, Ste 420, Los Angeles CA 90025
Email: mhmd@verizon.net
Address: 11600 Wilshire Blvd, Ste 420, Los Angeles CA 90025
Email: mhmd@verizon.net
HOURS OF OPERATION
| Mon-Fri 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM | |
| Sat-Sun - Closed |
PAYMENT OPTIONS



BROWSE OUR WEBSITE
CONTACT INFORMATION
Phone: (310) 477-7201
Address: 11600 Wilshire Blvd, Ste 420, Los Angeles CA 90025
Email: mhmd@verizon.net
Address: 11600 Wilshire Blvd, Ste 420, Los Angeles CA 90025
Email: mhmd@verizon.net
HOURS OF OPERATION
| Mon-Fri 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM | |
| Sat-Sun - Closed |
PAYMENT OPTIONS